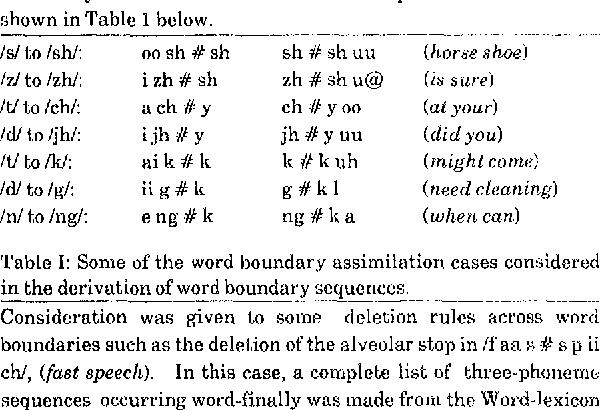
Speech Work: Word boundaries: production of sounds with reference to linking sounds.
Assimilation is the influence of a sound on a neighboring sound so that the two become similar or the same. Assimilation is a common phonological process by which the sound of the ending of one word blends into the sound of the beginning of the following word. This occurs when the parts of the mouth and vocal cords start to form the beginning sounds of the next word before the last sound has been completed. An example of this would be ‘hot potato’. The (t) in ‘hot’ is dropped as the lips prepare for the (p) sound for ‘potato’ (Bloomer et, 2005).
/ t / changes to / p / before / m / / b / or / p /
| basket maker | mixed bag |
| best man | mixed blessing |
| cat burglar | mixed marriage |
/ d / changes to / b / before / m / / b / or / p /
| bad pain | good cook |
| blood bank | good morning |
| bloodbath | grandmaster |
Differences between Polar and Tag Questions
In English, there are two basic forms of question: polar and non-polar:
Polar questions also called yes-or-no questions, i.e. questions that can be answered simply in the affirmative or negative. These questions normally invert the subject and verb:
- “His name is Ralph.” → “Is his name Ralph?”
- “You are sober enough to drive.” → “Are you sober enough to drive?”
- “That is what you’re wearing tonight.” → “Is that what you’re wearing tonight?”
Tag questions are something like negative questions. They are used when someone thinks he or she knows an answer and wants confirmation. There are two very commonly used types of tag questions; one made from affirmative (+ ) sentences, the other made from negative ( – ) sentences:
· He’s from Italy, isn’t he? /
· He isn’t from Italy, is he?
· She’s living in London, isn’t she? /
· She isn’t living in London, is she?
Tag questions append a word or phrase to a declarative sentence, asking for affirmation:
“It’s hot, isn’t it?”
“You wanted me to say that, didn’t you?”
Another difference between polar questions and the question tag is that in polar questions, the speaker does not know the answer to the question, and desire an answer, while in the question tag, the speaker has an idea of the answer but needs confirmation.
Composition: Expository Essay: How to Plant a tree
Follow the guidelines given to you earlier on how to write an expository essay
Literature-in-English: Use of Simile and Metaphor in sentences
A simile is described as the indirect comparison of two objects, persons or entities with the use of ‘as’ and ‘like’. Examples of simile in sentences:
· Ade’s head is as big as his house.
· Tayo is as stronger as a horse.
· Seeing you today is just like a dream to me.
· My nephew’s eye is like that of a cat.
· The policeman is as black as coal.
Metaphor, on the other hand, is referred to as the direct comparison of two things. The difference between simile and metaphor is that while one compares directly the other compares indirectly.
· David is a lion when it comes to fighting.
· My sister is a man when it comes to hard work.
· James is a goat, he is very stubborn.
· The man is a horse, he has so much strength.
· Mr. Frank is a chicken when it comes to facing challenges.
ASSESSMENT
- What is an Assimilation
- Define a metaphor
- Define a simile

